Publications
Fang, Lichen; Yan, Yishu; Agarwal, Ojaswi; Yao, Shengyu; Seppala, Jonathan E.; Kang, Sung Hoon
Effects of Environmental Temperature and Humidity on the Geometry and Strength of Polycarbonate Specimens Prepared by Fused Filament Fabrication Journal Article
In: Materials , vol. 13, no. 19, 2020.
@article{Fang2020b,
title = {Effects of Environmental Temperature and Humidity on the Geometry and Strength of Polycarbonate Specimens Prepared by Fused Filament Fabrication},
author = {Lichen Fang and Yishu Yan and Ojaswi Agarwal and Shengyu Yao and Jonathan E. Seppala and Sung Hoon Kang
},
url = {https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/13/19/4414},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194414},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-10-03},
journal = {Materials },
volume = {13},
number = {19},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Dagro, A.; Ramesh, K.; Venkatesan, A.; Kang, S. H.; Orrego, S.; Rajbhandari, L.
Quantifying the local mechanical properties of cells in a fibrous three-dimensional microenvironment Journal Article
In: Biophysical Journal, vol. 117, pp. 817-828, 2019.
@article{Dagro2019,
title = {Quantifying the local mechanical properties of cells in a fibrous three-dimensional microenvironment},
author = {A. Dagro and K. Ramesh and A. Venkatesan and S. H. Kang and S. Orrego and L. Rajbhandari},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006349519306319#fig1},
doi = {10.1016/j.bpj.2019.07.042},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-09-03},
journal = {Biophysical Journal},
volume = {117},
pages = {817-828},
abstract = {Measurements of the mechanical response of biological cells are critical for understanding injury and disease, for developing diagnostic tools, and for computational models in mechanobiology. Although it is well known that cells are sensitive to the topography of their microenvironment, the current paradigm in mechanical testing of adherent cells is mostly limited to specimens grown on flat two-dimensional substrates. In this study, we introduce a technique in which cellular indentation via optical trapping is performed on cells at a high spatial resolution to obtain their regional mechanical properties while they exist in a more favorable three-dimensional microenvironment. We combine our approach with nonlinear contact mechanics theory to consider the effects of a large deformation. This allows us to probe length scales that are relevant for obtaining overall cell stiffness values. The experimental results herein provide the hyperelastic material properties at both high (∼100 s−1) and low (∼1–10 s−1) strain rates of murine central nervous system glial cells. The limitations due to possible misalignment of the indenter in the three-dimensional space are examined using a computational model.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Note: Send e-mail to Prof. Kang at shkang@jhu.edu if you need a pdf file of the papers below.
2020
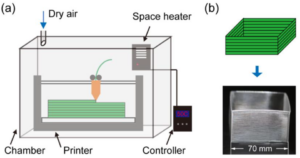
Fang, Lichen; Yan, Yishu; Agarwal, Ojaswi; Yao, Shengyu; Seppala, Jonathan E.; Kang, Sung Hoon
Effects of Environmental Temperature and Humidity on the Geometry and Strength of Polycarbonate Specimens Prepared by Fused Filament Fabrication Journal Article
In: Materials , vol. 13, no. 19, 2020.
Links | BibTeX | Tags: 3D printing, humidity, mechanical properties, modulus, temperature, toughness
@article{Fang2020b,
title = {Effects of Environmental Temperature and Humidity on the Geometry and Strength of Polycarbonate Specimens Prepared by Fused Filament Fabrication},
author = {Lichen Fang and Yishu Yan and Ojaswi Agarwal and Shengyu Yao and Jonathan E. Seppala and Sung Hoon Kang
},
url = {https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/13/19/4414},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194414},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-10-03},
journal = {Materials },
volume = {13},
number = {19},
keywords = {3D printing, humidity, mechanical properties, modulus, temperature, toughness},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2019
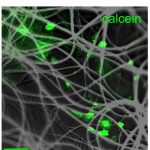
Dagro, A.; Ramesh, K.; Venkatesan, A.; Kang, S. H.; Orrego, S.; Rajbhandari, L.
Quantifying the local mechanical properties of cells in a fibrous three-dimensional microenvironment Journal Article
In: Biophysical Journal, vol. 117, pp. 817-828, 2019.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: 3D, cells, electrospinning, fiber, mechanical properties, microenvironment
@article{Dagro2019,
title = {Quantifying the local mechanical properties of cells in a fibrous three-dimensional microenvironment},
author = {A. Dagro and K. Ramesh and A. Venkatesan and S. H. Kang and S. Orrego and L. Rajbhandari},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006349519306319#fig1},
doi = {10.1016/j.bpj.2019.07.042},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-09-03},
journal = {Biophysical Journal},
volume = {117},
pages = {817-828},
abstract = {Measurements of the mechanical response of biological cells are critical for understanding injury and disease, for developing diagnostic tools, and for computational models in mechanobiology. Although it is well known that cells are sensitive to the topography of their microenvironment, the current paradigm in mechanical testing of adherent cells is mostly limited to specimens grown on flat two-dimensional substrates. In this study, we introduce a technique in which cellular indentation via optical trapping is performed on cells at a high spatial resolution to obtain their regional mechanical properties while they exist in a more favorable three-dimensional microenvironment. We combine our approach with nonlinear contact mechanics theory to consider the effects of a large deformation. This allows us to probe length scales that are relevant for obtaining overall cell stiffness values. The experimental results herein provide the hyperelastic material properties at both high (∼100 s−1) and low (∼1–10 s−1) strain rates of murine central nervous system glial cells. The limitations due to possible misalignment of the indenter in the three-dimensional space are examined using a computational model.},
keywords = {3D, cells, electrospinning, fiber, mechanical properties, microenvironment},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}