Publications
Liu, Jia; Gu, Tianyu; Shan, Sicong; Kang, Sung H.; Weaver, James C.; Bertoldi, Katia
Harnessing Buckling to Design Architected Materials that Exhibit Effective Negative Swelling Journal Article
In: Advanced Materials, vol. 28, pp. 6619–6624, 2016.
@article{Liu2016,
title = {Harnessing Buckling to Design Architected Materials that Exhibit Effective Negative Swelling},
author = {Jia Liu and Tianyu Gu and Sicong Shan and Sung H. Kang and James C. Weaver and Katia Bertoldi},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201600812/pdf},
doi = {10.1002/adma.201600812},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-05-17},
journal = {Advanced Materials},
volume = {28},
pages = {6619–6624},
abstract = {Inspired by the need to develop materials capable of targeted and extreme volume changes during operation, numerical simulations and experiments are combined to design a new class of soft architected materials that achieve a reduction of projected surface area coverage during swelling. },
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Shan, Sicong; Kang, Sung Hoon; Wang, Pai; Qu, Cangyu; Shian, Samuel; Chen, Elizabeth R.; Weaver, James C.; Bertoldi, Katia
Harnessing Multiple Folding Mechanisms in Soft Periodic and Porous Structures to Design Highly Tunable Phononic Crystals Journal Article
In: Advanced Functional Materials, vol. 24, pp. 4935–4942, 2014.
@article{Shan2014,
title = {Harnessing Multiple Folding Mechanisms in Soft Periodic and Porous Structures to Design Highly Tunable Phononic Crystals},
author = {Sicong Shan and Sung Hoon Kang and Pai Wang and Cangyu Qu and Samuel Shian and Elizabeth R. Chen and James C. Weaver and Katia Bertoldi},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adfm.201400665/abstract},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-08-20},
journal = {Advanced Functional Materials},
volume = {24},
pages = {4935–4942},
abstract = {Mechanical instabilities in periodic porous elastic structures may lead to the formation of homogeneous patterns, opening avenues for a wide range of applications that are related to the geometry of the system. This study focuses on an elastomeric porous structure comprising a triangular array of circular holes, and shows that by controlling the loading direction, multiple pattern transformations can be induced by buckling. Interestingly, these different pattern transformations can be exploited to design materials with highly tunable properties. In particular, these results indicate that they can be effectively used to tune the propagation of elastic waves in phononic crystals, enhancing the tunability of the dynamic response of the system. Using a combination of finite element simulations and experiments, a proof-of-concept of the novel material is demonstrated. Since the proposed mechanism is induced by elastic instability, it is reversible, repeatable, and scale-independent, opening avenues for the design of highly tunable materials and devices over a wide range of length scales.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Shim, Jongmin; Shan, Sicong; Kosmrlj, Andrej; Kang, Sung Hoon; Chen, Elizabeth R.; Weaver, James C.; Bertoldi, Katia
Harnessing Instabilities for Design of Soft Reconfigurable Auxetic/Chiral Materials Journal Article
In: Soft Matter, vol. 9, pp. 8198-8202, 2013, (Highlighted on the Soft Matter blog.).
@article{Shim2013,
title = {Harnessing Instabilities for Design of Soft Reconfigurable Auxetic/Chiral Materials},
author = {Jongmin Shim and Sicong Shan and Andrej Kosmrlj and Sung Hoon Kang and Elizabeth R. Chen and James C. Weaver and Katia Bertoldi},
url = {http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2013/sm/c3sm51148k#!divAbstract},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-05-31},
journal = {Soft Matter},
volume = {9},
pages = {8198-8202},
abstract = {Most materials have a unique form optimized for a specific property and function. However, the ability to reconfigure material structures depending on stimuli opens exciting opportunities. Although mechanical instabilities have been traditionally viewed as a failure mode, here we exploit them to design a class of 2D soft materials whose architecture can be dramatically changed in response to an external stimulus. By considering geometric constraints on the tessellations of the 2D Euclidean plane, we have identified four possible periodic distributions of uniform circular holes where mechanical instability can be exploited to reversibly switch between expanded (i.e. with circular holes) and compact (i.e. with elongated, almost closed elliptical holes) periodic configurations. Interestingly, in all these structures buckling is found to induce large negative values of incremental Poisson's ratio and in two of them also the formation of chiral patterns. Using a combination of finite element simulations and experiments at the centimeter scale we demonstrate a proof-of-concept of the proposed materials. Since the proposed mechanism for reconfigurable materials is induced by elastic instability, it is reversible, repeatable and scale-independent.},
note = {Highlighted on the Soft Matter blog.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Note: Send e-mail to Prof. Kang at shkang@jhu.edu if you need a pdf file of the papers below.
2016
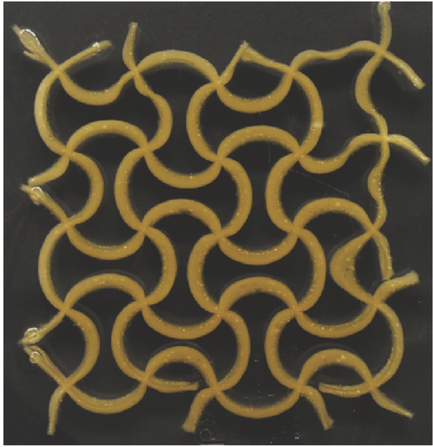

Liu, Jia; Gu, Tianyu; Shan, Sicong; Kang, Sung H.; Weaver, James C.; Bertoldi, Katia
Harnessing Buckling to Design Architected Materials that Exhibit Effective Negative Swelling Journal Article
In: Advanced Materials, vol. 28, pp. 6619–6624, 2016.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: architected materials, Mechanical Instability, mechanics of soft materials and structures, Reversible, Soft Periodic Porous Structures
@article{Liu2016,
title = {Harnessing Buckling to Design Architected Materials that Exhibit Effective Negative Swelling},
author = {Jia Liu and Tianyu Gu and Sicong Shan and Sung H. Kang and James C. Weaver and Katia Bertoldi},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201600812/pdf},
doi = {10.1002/adma.201600812},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-05-17},
journal = {Advanced Materials},
volume = {28},
pages = {6619–6624},
abstract = {Inspired by the need to develop materials capable of targeted and extreme volume changes during operation, numerical simulations and experiments are combined to design a new class of soft architected materials that achieve a reduction of projected surface area coverage during swelling. },
keywords = {architected materials, Mechanical Instability, mechanics of soft materials and structures, Reversible, Soft Periodic Porous Structures},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2014
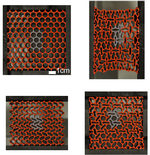
Shan, Sicong; Kang, Sung Hoon; Wang, Pai; Qu, Cangyu; Shian, Samuel; Chen, Elizabeth R.; Weaver, James C.; Bertoldi, Katia
Harnessing Multiple Folding Mechanisms in Soft Periodic and Porous Structures to Design Highly Tunable Phononic Crystals Journal Article
In: Advanced Functional Materials, vol. 24, pp. 4935–4942, 2014.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: 3D printing, architected materials, Folding Mechanismsm, mechanics of soft materials and structures, Metamaterial, Phononic Crystals, Soft Periodic Porous Structures, Tunability
@article{Shan2014,
title = {Harnessing Multiple Folding Mechanisms in Soft Periodic and Porous Structures to Design Highly Tunable Phononic Crystals},
author = {Sicong Shan and Sung Hoon Kang and Pai Wang and Cangyu Qu and Samuel Shian and Elizabeth R. Chen and James C. Weaver and Katia Bertoldi},
url = {http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adfm.201400665/abstract},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-08-20},
journal = {Advanced Functional Materials},
volume = {24},
pages = {4935–4942},
abstract = {Mechanical instabilities in periodic porous elastic structures may lead to the formation of homogeneous patterns, opening avenues for a wide range of applications that are related to the geometry of the system. This study focuses on an elastomeric porous structure comprising a triangular array of circular holes, and shows that by controlling the loading direction, multiple pattern transformations can be induced by buckling. Interestingly, these different pattern transformations can be exploited to design materials with highly tunable properties. In particular, these results indicate that they can be effectively used to tune the propagation of elastic waves in phononic crystals, enhancing the tunability of the dynamic response of the system. Using a combination of finite element simulations and experiments, a proof-of-concept of the novel material is demonstrated. Since the proposed mechanism is induced by elastic instability, it is reversible, repeatable, and scale-independent, opening avenues for the design of highly tunable materials and devices over a wide range of length scales.},
keywords = {3D printing, architected materials, Folding Mechanismsm, mechanics of soft materials and structures, Metamaterial, Phononic Crystals, Soft Periodic Porous Structures, Tunability},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2013
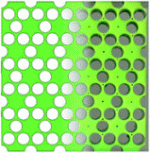
Shim, Jongmin; Shan, Sicong; Kosmrlj, Andrej; Kang, Sung Hoon; Chen, Elizabeth R.; Weaver, James C.; Bertoldi, Katia
Harnessing Instabilities for Design of Soft Reconfigurable Auxetic/Chiral Materials Journal Article
In: Soft Matter, vol. 9, pp. 8198-8202, 2013, (Highlighted on the Soft Matter blog.).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: 3D printing, architected materials, Auxetic, Chiral, Mechanical Instability, mechanics of soft materials and structures, Metamaterial, Soft Periodic Porous Structures, Symmetry Breaking
@article{Shim2013,
title = {Harnessing Instabilities for Design of Soft Reconfigurable Auxetic/Chiral Materials},
author = {Jongmin Shim and Sicong Shan and Andrej Kosmrlj and Sung Hoon Kang and Elizabeth R. Chen and James C. Weaver and Katia Bertoldi},
url = {http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2013/sm/c3sm51148k#!divAbstract},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-05-31},
journal = {Soft Matter},
volume = {9},
pages = {8198-8202},
abstract = {Most materials have a unique form optimized for a specific property and function. However, the ability to reconfigure material structures depending on stimuli opens exciting opportunities. Although mechanical instabilities have been traditionally viewed as a failure mode, here we exploit them to design a class of 2D soft materials whose architecture can be dramatically changed in response to an external stimulus. By considering geometric constraints on the tessellations of the 2D Euclidean plane, we have identified four possible periodic distributions of uniform circular holes where mechanical instability can be exploited to reversibly switch between expanded (i.e. with circular holes) and compact (i.e. with elongated, almost closed elliptical holes) periodic configurations. Interestingly, in all these structures buckling is found to induce large negative values of incremental Poisson's ratio and in two of them also the formation of chiral patterns. Using a combination of finite element simulations and experiments at the centimeter scale we demonstrate a proof-of-concept of the proposed materials. Since the proposed mechanism for reconfigurable materials is induced by elastic instability, it is reversible, repeatable and scale-independent.},
note = {Highlighted on the Soft Matter blog.},
keywords = {3D printing, architected materials, Auxetic, Chiral, Mechanical Instability, mechanics of soft materials and structures, Metamaterial, Soft Periodic Porous Structures, Symmetry Breaking},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}