Publications
Mandal, Krishna C.; Kang, Sung Hoon; Choi, Michael; Kargar, Alireza; Harrison, Mark J.; McGregor, Douglas S.; Bolotnikov, Aleksey E.; Carini, Gabriella A.; Giuseppe C. Camarda,; James, Ralph B.
Characterization of Low-Defect Cd0.9Zn0.1Te and CdTe Crystals for High-Performance Frisch Collar Detectors Journal Article
In: IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, vol. 54, pp. 802 – 806 , 2007.
@article{Mandal2007,
title = {Characterization of Low-Defect Cd0.9Zn0.1Te and CdTe Crystals for High-Performance Frisch Collar Detectors},
author = {Krishna C. Mandal and Sung Hoon Kang and Michael Choi and Alireza Kargar and Mark J. Harrison and Douglas S. McGregor and Aleksey E. Bolotnikov and Gabriella A. Carini and Giuseppe C. Camarda, and Ralph B. James},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/login.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4291754&url=http%3A%2F%2Fieeexplore.ieee.org%2Fxpls%2Fabs_all.jsp%3Farnumber%3D4291754},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-08-20},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science},
volume = {54},
pages = {802 - 806 },
abstract = {Low dislocation density, high-purity, and low inclusion concentration Cd0.9Zn0.1Te (CZT) and CdTe crystals were grown by a vertical Bridgman technique using in-house zone refined precursors. The grown crystals were sequentially processed using optimized chemo-mechanical processes to fabricate planar and Frisch collar detectors. Infrared transmission and scanning electron microscopy studies have shown that EIC grown CZT and CdTe crystals have significantly lower Te inclusions and defect densities than commercially available spectrometer grade crystals. The charge transport properties (electron and hole mobility-lifetime products, mutaue & mutauh) of various detectors have been evaluated by Hecht analysis. The detectors have been tested for spectral response using 59.5 and 662 keV gamma-ray sources. The CZT detectors with planar electrodes showed 2.6% FWHM at 662 keV. By adding a Frisch collar, the detectors' spectra improved significantly. The Frisch collar detectors proved to be very promising for assembling large-area arrays with excellent energy resolution at relatively low manufacturing cost.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Mandal, Krishna C.; Kang, Sung Hoon; Choi, Michael; Bello, Job; Zheng, Lili; Zhang, Hui; Groza, Michael; Roy, Utpal N.; Burger, Arnold; Jellison, Gerald E.; Holcomb, David E.; Wright, Gomez W.; Williams, Joseph A.
Simulation, modeling, and crystal growth of Cd0.9Zn0.1Te for nuclear spectrometers Journal Article
In: Journal of Electronic Materials, vol. 35, pp. 1251-1256, 2006.
@article{Mandal2006,
title = {Simulation, modeling, and crystal growth of Cd0.9Zn0.1Te for nuclear spectrometers},
author = {Krishna C. Mandal and Sung Hoon Kang and Michael Choi and Job Bello and Lili Zheng and Hui Zhang and Michael Groza and Utpal N. Roy and Arnold Burger and Gerald E. Jellison and David E. Holcomb and Gomez W. Wright and Joseph A. Williams },
url = {http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11664-006-0250-6},
year = {2006},
date = {2006-06-01},
journal = {Journal of Electronic Materials},
volume = {35},
pages = {1251-1256},
abstract = {High-quality, large (10 cm long and 2.5 cm diameter), nuclear spectrometer grade Cd0.9Zn0.1Te (CZT) single crystals have been grown by a controlled vertical Bridgman technique using in-house zone refined precursor materials (Cd, Zn, and Te). A state-of-the-art computer model, multizone adaptive scheme for transport and phase-change processes (MASTRAP), is used to model heat and mass transfer in the Bridgman growth system and to predict the stress distribution in the as-grown CZT crystal and optimize the thermal profile. The model accounts for heat transfer in the multiphase system, convection in the melt, and interface dynamics. The grown semi-insulating (SI) CZT crystals have demonstrated promising results for high-resolution room-temperature radiation detectors due to their high dark resistivity (ρ≈2.8 × 1011 Θ cm), good charge-transport properties [electron and hole mobility-life-time product, μτe≈(2–5)×10−3 and μτh≈(3–5)×10−5 respectively, and low cost of production. Spectroscopic ellipsometry and optical transmission measurements were carried out on the grown CZT crystals using two-modulator generalized ellipsometry (2-MGE). The refractive index n and extinction coefficient k were determined by mathematically eliminating the ∼3-nm surface roughness layer. Nuclear detection measurements on the single-element CZT detectors with 241Am and 137Cs clearly detected 59.6 and 662 keV energies with energy resolution (FWHM) of 2.4 keV (4.0%) and 9.2 keV (1.4%), respectively.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Note: Send e-mail to Prof. Kang at shkang@jhu.edu if you need a pdf file of the papers below.
2007
Mandal, Krishna C.; Kang, Sung Hoon; Choi, Michael; Kargar, Alireza; Harrison, Mark J.; McGregor, Douglas S.; Bolotnikov, Aleksey E.; Carini, Gabriella A.; Giuseppe C. Camarda,; James, Ralph B.
Characterization of Low-Defect Cd0.9Zn0.1Te and CdTe Crystals for High-Performance Frisch Collar Detectors Journal Article
In: IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, vol. 54, pp. 802 – 806 , 2007.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: CdTe, Characterization, Crystal, CZT, Detector
@article{Mandal2007,
title = {Characterization of Low-Defect Cd0.9Zn0.1Te and CdTe Crystals for High-Performance Frisch Collar Detectors},
author = {Krishna C. Mandal and Sung Hoon Kang and Michael Choi and Alireza Kargar and Mark J. Harrison and Douglas S. McGregor and Aleksey E. Bolotnikov and Gabriella A. Carini and Giuseppe C. Camarda, and Ralph B. James},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/login.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4291754&url=http%3A%2F%2Fieeexplore.ieee.org%2Fxpls%2Fabs_all.jsp%3Farnumber%3D4291754},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-08-20},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science},
volume = {54},
pages = {802 - 806 },
abstract = {Low dislocation density, high-purity, and low inclusion concentration Cd0.9Zn0.1Te (CZT) and CdTe crystals were grown by a vertical Bridgman technique using in-house zone refined precursors. The grown crystals were sequentially processed using optimized chemo-mechanical processes to fabricate planar and Frisch collar detectors. Infrared transmission and scanning electron microscopy studies have shown that EIC grown CZT and CdTe crystals have significantly lower Te inclusions and defect densities than commercially available spectrometer grade crystals. The charge transport properties (electron and hole mobility-lifetime products, mutaue & mutauh) of various detectors have been evaluated by Hecht analysis. The detectors have been tested for spectral response using 59.5 and 662 keV gamma-ray sources. The CZT detectors with planar electrodes showed 2.6% FWHM at 662 keV. By adding a Frisch collar, the detectors' spectra improved significantly. The Frisch collar detectors proved to be very promising for assembling large-area arrays with excellent energy resolution at relatively low manufacturing cost.},
keywords = {CdTe, Characterization, Crystal, CZT, Detector},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2006
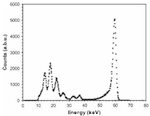
Mandal, Krishna C.; Kang, Sung Hoon; Choi, Michael; Bello, Job; Zheng, Lili; Zhang, Hui; Groza, Michael; Roy, Utpal N.; Burger, Arnold; Jellison, Gerald E.; Holcomb, David E.; Wright, Gomez W.; Williams, Joseph A.
Simulation, modeling, and crystal growth of Cd0.9Zn0.1Te for nuclear spectrometers Journal Article
In: Journal of Electronic Materials, vol. 35, pp. 1251-1256, 2006.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Crystal, CZT, Growth, Modeling, Simulation, spectrometer
@article{Mandal2006,
title = {Simulation, modeling, and crystal growth of Cd0.9Zn0.1Te for nuclear spectrometers},
author = {Krishna C. Mandal and Sung Hoon Kang and Michael Choi and Job Bello and Lili Zheng and Hui Zhang and Michael Groza and Utpal N. Roy and Arnold Burger and Gerald E. Jellison and David E. Holcomb and Gomez W. Wright and Joseph A. Williams },
url = {http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11664-006-0250-6},
year = {2006},
date = {2006-06-01},
journal = {Journal of Electronic Materials},
volume = {35},
pages = {1251-1256},
abstract = {High-quality, large (10 cm long and 2.5 cm diameter), nuclear spectrometer grade Cd0.9Zn0.1Te (CZT) single crystals have been grown by a controlled vertical Bridgman technique using in-house zone refined precursor materials (Cd, Zn, and Te). A state-of-the-art computer model, multizone adaptive scheme for transport and phase-change processes (MASTRAP), is used to model heat and mass transfer in the Bridgman growth system and to predict the stress distribution in the as-grown CZT crystal and optimize the thermal profile. The model accounts for heat transfer in the multiphase system, convection in the melt, and interface dynamics. The grown semi-insulating (SI) CZT crystals have demonstrated promising results for high-resolution room-temperature radiation detectors due to their high dark resistivity (ρ≈2.8 × 1011 Θ cm), good charge-transport properties [electron and hole mobility-life-time product, μτe≈(2–5)×10−3 and μτh≈(3–5)×10−5 respectively, and low cost of production. Spectroscopic ellipsometry and optical transmission measurements were carried out on the grown CZT crystals using two-modulator generalized ellipsometry (2-MGE). The refractive index n and extinction coefficient k were determined by mathematically eliminating the ∼3-nm surface roughness layer. Nuclear detection measurements on the single-element CZT detectors with 241Am and 137Cs clearly detected 59.6 and 662 keV energies with energy resolution (FWHM) of 2.4 keV (4.0%) and 9.2 keV (1.4%), respectively.},
keywords = {Crystal, CZT, Growth, Modeling, Simulation, spectrometer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}