Publications
Pokroy, Boaz; Aichmayer, Barbara; Schenk, Anna S.; Haimov, Boris; Kang, Sung Hoon; Fratzl, Peter; Aizenberg, Joanna
Sonication-Assisted Synthesis of Large, High-Quality Mercury-Thiolate Single Crystals Directly from Liquid Mercury Journal Article
In: Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 132, pp. 14355–14357, 2010, (Highlighted on C&EN.).
@article{Pokroy2010,
title = {Sonication-Assisted Synthesis of Large, High-Quality Mercury-Thiolate Single Crystals Directly from Liquid Mercury},
author = {Boaz Pokroy and Barbara Aichmayer and Anna S. Schenk and Boris Haimov and Sung Hoon Kang and Peter Fratzl and Joanna Aizenberg},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ja1056449},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-09-27},
journal = {Journal of the American Chemical Society},
volume = {132},
pages = {14355–14357},
abstract = {The synthetic formation of mercury thiolates has been known for almost 200 years. These compounds are usually formed by a slow reaction of mercury salts with thiolates or disulfides to produce small (up to 1 μm), plate-like crystals of Hg(S-R)2. Herein we show that such mercury thiolates can be formed directly from liquid mercury via sonication with neat thiols. The process not only produces crystals very rapidly (within seconds) but also leads to the formation of large crystals (up to hundreds of micrometers). The high quality of these crystals enabled their detailed structural characterization, which showed that the crystals are composed of ordered Hg(thiol)2 stacks. We extended the experimental procedure to form and characterize a range of Hg thiolate crystals with various chain lengths. We propose a new self-assembly mechanism that can explain how sonication—which is usually used to break chemical bonds, to disperse materials, and to form nanosized crystallites—may lead to the growth of large, high-quality crystals.},
note = {Highlighted on C&EN.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Mandal, Krishna C.; Kang, Sung Hoon; Choi, Michael; Chen, Jian; Zhang, Xi-Cheng; Schleicher, James M.; Schmuttenmaer, Charles A.; Fernelius, Nils C.
III–VI Chalcogenide Semiconductor Crystals for Broadband Tunable THz Sources and Sensors Journal Article
In: IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, vol. 14, pp. 284 – 288, 2008.
@article{Mandal2008,
title = {III–VI Chalcogenide Semiconductor Crystals for Broadband Tunable THz Sources and Sensors},
author = {Krishna C. Mandal and Sung Hoon Kang and Michael Choi and Jian Chen and Xi-Cheng Zhang and James M. Schleicher and Charles A. Schmuttenmaer and Nils C. Fernelius},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?reload=true&arnumber=4481122},
year = {2008},
date = {2008-04-04},
journal = {IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics},
volume = {14},
pages = {284 - 288},
abstract = {The layered chalcogenide semiconductor GaSe has been grown under various crystal growth conditions for optimum performance for tunable terahertz (THz) wave generation and broadband THz detection. Low-temperature photoluminescence (PL), Raman spectroscopy, optical absorption/transmission, electrical charge transport property measurements, and THz time-domain spectroscopy (TDS) have been used to characterize the grown crystals. It is observed that indium doping enhances hardness of the grown GaSe crystals, which is very useful for processing and fabricating large-area devices. GaSe crystals have demonstrated promising characteristics with good optical quality (absorption coefficient les0.1 cm-1 in the spectral range of 0.62-18 mum), high dark resistivity (ges109 Omega cm), wide bandgap (2.01 eV at 300 K), good anisotropic (parand perp) electrical transport properties (mue/h, taue/h, and mutaue/h) and long-term stability. The THz emission measurements have shown that the GaSe crystals are highly efficient for broadband tunable THz sources (up to 40 THz), and sensors (up to 100 THz). Additionally, new THz frequencies (0.1-3 THz) have been observed for the first time from an anisotropic binary and a ternary semiconductor crystal. Details of characterizations as well as optimum crystal growth conditions including simulation and computer modeling are described in this paper.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Mandal, Krishna C.; Kang, Sung Hoon; Choi, Michael; Kargar, Alireza; Harrison, Mark J.; McGregor, Douglas S.; Bolotnikov, Aleksey E.; Carini, Gabriella A.; Giuseppe C. Camarda,; James, Ralph B.
Characterization of Low-Defect Cd0.9Zn0.1Te and CdTe Crystals for High-Performance Frisch Collar Detectors Journal Article
In: IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, vol. 54, pp. 802 – 806 , 2007.
@article{Mandal2007,
title = {Characterization of Low-Defect Cd0.9Zn0.1Te and CdTe Crystals for High-Performance Frisch Collar Detectors},
author = {Krishna C. Mandal and Sung Hoon Kang and Michael Choi and Alireza Kargar and Mark J. Harrison and Douglas S. McGregor and Aleksey E. Bolotnikov and Gabriella A. Carini and Giuseppe C. Camarda, and Ralph B. James},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/login.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4291754&url=http%3A%2F%2Fieeexplore.ieee.org%2Fxpls%2Fabs_all.jsp%3Farnumber%3D4291754},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-08-20},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science},
volume = {54},
pages = {802 - 806 },
abstract = {Low dislocation density, high-purity, and low inclusion concentration Cd0.9Zn0.1Te (CZT) and CdTe crystals were grown by a vertical Bridgman technique using in-house zone refined precursors. The grown crystals were sequentially processed using optimized chemo-mechanical processes to fabricate planar and Frisch collar detectors. Infrared transmission and scanning electron microscopy studies have shown that EIC grown CZT and CdTe crystals have significantly lower Te inclusions and defect densities than commercially available spectrometer grade crystals. The charge transport properties (electron and hole mobility-lifetime products, mutaue & mutauh) of various detectors have been evaluated by Hecht analysis. The detectors have been tested for spectral response using 59.5 and 662 keV gamma-ray sources. The CZT detectors with planar electrodes showed 2.6% FWHM at 662 keV. By adding a Frisch collar, the detectors' spectra improved significantly. The Frisch collar detectors proved to be very promising for assembling large-area arrays with excellent energy resolution at relatively low manufacturing cost.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Mandal, Krishna C.; Kang, Sung Hoon; Choi, Michael; Wei, Jiuan; Zheng, Lili; Zhang, Hui; Jellison, Gerald E.; Groza, Michael; Burger, Arnold
Component Overpressure Growth and Characterization of High-Resistivity CdTe Crystals for Radiation Detectors Journal Article
In: Journal of Electronic Materials, vol. 36, pp. 1013-1020, 2007.
@article{Mandal2007b,
title = {Component Overpressure Growth and Characterization of High-Resistivity CdTe Crystals for Radiation Detectors},
author = {Krishna C. Mandal and Sung Hoon Kang and Michael Choi and Jiuan Wei and Lili Zheng and Hui Zhang and Gerald E. Jellison and Michael Groza and Arnold Burger },
url = {http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11664-007-0164-y},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-07-06},
journal = {Journal of Electronic Materials},
volume = {36},
pages = {1013-1020},
abstract = {Spectrometer-grade CdTe single crystals with resistivities higher than 109 Ω cm have been grown by the modified Bridgman method using zone-refined precursor materials (Cd and Te) under a Cd overpressure. The grown CdTe crystals had good charge-transport properties (μτ e = 2 × 10−3 cm2 V−1, μτ h = 8 × 10−5 cm2 V−1) and significantly reduced Te precipitates compared with crystals grown without Cd overpressure. The crystal growth conditions for the Bridgman system were optimized by computer modeling and simulation, using modified MASTRAPP program, and applied to crystal diameters of 14 mm (0.55′′), 38 mm (1.5′′), and 76 mm (3′′). Details of the CdTe crystal growth operation, structural, electrical, and optical characterization measurements, detector fabrication, and testing using 241Am (60 keV) and 137Cs (662 keV) sources are presented.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Mandal, Krishna C.; Kang, Sung Hoon; Choi, Michael; Bello, Job; Zheng, Lili; Zhang, Hui; Groza, Michael; Roy, Utpal N.; Burger, Arnold; Jellison, Gerald E.; Holcomb, David E.; Wright, Gomez W.; Williams, Joseph A.
Simulation, modeling, and crystal growth of Cd0.9Zn0.1Te for nuclear spectrometers Journal Article
In: Journal of Electronic Materials, vol. 35, pp. 1251-1256, 2006.
@article{Mandal2006,
title = {Simulation, modeling, and crystal growth of Cd0.9Zn0.1Te for nuclear spectrometers},
author = {Krishna C. Mandal and Sung Hoon Kang and Michael Choi and Job Bello and Lili Zheng and Hui Zhang and Michael Groza and Utpal N. Roy and Arnold Burger and Gerald E. Jellison and David E. Holcomb and Gomez W. Wright and Joseph A. Williams },
url = {http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11664-006-0250-6},
year = {2006},
date = {2006-06-01},
journal = {Journal of Electronic Materials},
volume = {35},
pages = {1251-1256},
abstract = {High-quality, large (10 cm long and 2.5 cm diameter), nuclear spectrometer grade Cd0.9Zn0.1Te (CZT) single crystals have been grown by a controlled vertical Bridgman technique using in-house zone refined precursor materials (Cd, Zn, and Te). A state-of-the-art computer model, multizone adaptive scheme for transport and phase-change processes (MASTRAP), is used to model heat and mass transfer in the Bridgman growth system and to predict the stress distribution in the as-grown CZT crystal and optimize the thermal profile. The model accounts for heat transfer in the multiphase system, convection in the melt, and interface dynamics. The grown semi-insulating (SI) CZT crystals have demonstrated promising results for high-resolution room-temperature radiation detectors due to their high dark resistivity (ρ≈2.8 × 1011 Θ cm), good charge-transport properties [electron and hole mobility-life-time product, μτe≈(2–5)×10−3 and μτh≈(3–5)×10−5 respectively, and low cost of production. Spectroscopic ellipsometry and optical transmission measurements were carried out on the grown CZT crystals using two-modulator generalized ellipsometry (2-MGE). The refractive index n and extinction coefficient k were determined by mathematically eliminating the ∼3-nm surface roughness layer. Nuclear detection measurements on the single-element CZT detectors with 241Am and 137Cs clearly detected 59.6 and 662 keV energies with energy resolution (FWHM) of 2.4 keV (4.0%) and 9.2 keV (1.4%), respectively.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Note: Send e-mail to Prof. Kang at shkang@jhu.edu if you need a pdf file of the papers below.
2010
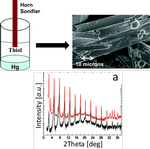
Pokroy, Boaz; Aichmayer, Barbara; Schenk, Anna S.; Haimov, Boris; Kang, Sung Hoon; Fratzl, Peter; Aizenberg, Joanna
Sonication-Assisted Synthesis of Large, High-Quality Mercury-Thiolate Single Crystals Directly from Liquid Mercury Journal Article
In: Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 132, pp. 14355–14357, 2010, (Highlighted on C&EN.).
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Crystal, Mercury Thiolate, Single Crystal, Sonication, Synthesis
@article{Pokroy2010,
title = {Sonication-Assisted Synthesis of Large, High-Quality Mercury-Thiolate Single Crystals Directly from Liquid Mercury},
author = {Boaz Pokroy and Barbara Aichmayer and Anna S. Schenk and Boris Haimov and Sung Hoon Kang and Peter Fratzl and Joanna Aizenberg},
url = {http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ja1056449},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-09-27},
journal = {Journal of the American Chemical Society},
volume = {132},
pages = {14355–14357},
abstract = {The synthetic formation of mercury thiolates has been known for almost 200 years. These compounds are usually formed by a slow reaction of mercury salts with thiolates or disulfides to produce small (up to 1 μm), plate-like crystals of Hg(S-R)2. Herein we show that such mercury thiolates can be formed directly from liquid mercury via sonication with neat thiols. The process not only produces crystals very rapidly (within seconds) but also leads to the formation of large crystals (up to hundreds of micrometers). The high quality of these crystals enabled their detailed structural characterization, which showed that the crystals are composed of ordered Hg(thiol)2 stacks. We extended the experimental procedure to form and characterize a range of Hg thiolate crystals with various chain lengths. We propose a new self-assembly mechanism that can explain how sonication—which is usually used to break chemical bonds, to disperse materials, and to form nanosized crystallites—may lead to the growth of large, high-quality crystals.},
note = {Highlighted on C&EN.},
keywords = {Crystal, Mercury Thiolate, Single Crystal, Sonication, Synthesis},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2008
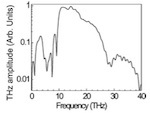
Mandal, Krishna C.; Kang, Sung Hoon; Choi, Michael; Chen, Jian; Zhang, Xi-Cheng; Schleicher, James M.; Schmuttenmaer, Charles A.; Fernelius, Nils C.
III–VI Chalcogenide Semiconductor Crystals for Broadband Tunable THz Sources and Sensors Journal Article
In: IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, vol. 14, pp. 284 – 288, 2008.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Broadband, Chalcogenide, Crystal, III-VI, Semiconductor, Sensor, Source, THz, Tunable
@article{Mandal2008,
title = {III–VI Chalcogenide Semiconductor Crystals for Broadband Tunable THz Sources and Sensors},
author = {Krishna C. Mandal and Sung Hoon Kang and Michael Choi and Jian Chen and Xi-Cheng Zhang and James M. Schleicher and Charles A. Schmuttenmaer and Nils C. Fernelius},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?reload=true&arnumber=4481122},
year = {2008},
date = {2008-04-04},
journal = {IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics},
volume = {14},
pages = {284 - 288},
abstract = {The layered chalcogenide semiconductor GaSe has been grown under various crystal growth conditions for optimum performance for tunable terahertz (THz) wave generation and broadband THz detection. Low-temperature photoluminescence (PL), Raman spectroscopy, optical absorption/transmission, electrical charge transport property measurements, and THz time-domain spectroscopy (TDS) have been used to characterize the grown crystals. It is observed that indium doping enhances hardness of the grown GaSe crystals, which is very useful for processing and fabricating large-area devices. GaSe crystals have demonstrated promising characteristics with good optical quality (absorption coefficient les0.1 cm-1 in the spectral range of 0.62-18 mum), high dark resistivity (ges109 Omega cm), wide bandgap (2.01 eV at 300 K), good anisotropic (parand perp) electrical transport properties (mue/h, taue/h, and mutaue/h) and long-term stability. The THz emission measurements have shown that the GaSe crystals are highly efficient for broadband tunable THz sources (up to 40 THz), and sensors (up to 100 THz). Additionally, new THz frequencies (0.1-3 THz) have been observed for the first time from an anisotropic binary and a ternary semiconductor crystal. Details of characterizations as well as optimum crystal growth conditions including simulation and computer modeling are described in this paper.},
keywords = {Broadband, Chalcogenide, Crystal, III-VI, Semiconductor, Sensor, Source, THz, Tunable},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2007
Mandal, Krishna C.; Kang, Sung Hoon; Choi, Michael; Kargar, Alireza; Harrison, Mark J.; McGregor, Douglas S.; Bolotnikov, Aleksey E.; Carini, Gabriella A.; Giuseppe C. Camarda,; James, Ralph B.
Characterization of Low-Defect Cd0.9Zn0.1Te and CdTe Crystals for High-Performance Frisch Collar Detectors Journal Article
In: IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, vol. 54, pp. 802 – 806 , 2007.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: CdTe, Characterization, Crystal, CZT, Detector
@article{Mandal2007,
title = {Characterization of Low-Defect Cd0.9Zn0.1Te and CdTe Crystals for High-Performance Frisch Collar Detectors},
author = {Krishna C. Mandal and Sung Hoon Kang and Michael Choi and Alireza Kargar and Mark J. Harrison and Douglas S. McGregor and Aleksey E. Bolotnikov and Gabriella A. Carini and Giuseppe C. Camarda, and Ralph B. James},
url = {http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/login.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4291754&url=http%3A%2F%2Fieeexplore.ieee.org%2Fxpls%2Fabs_all.jsp%3Farnumber%3D4291754},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-08-20},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science},
volume = {54},
pages = {802 - 806 },
abstract = {Low dislocation density, high-purity, and low inclusion concentration Cd0.9Zn0.1Te (CZT) and CdTe crystals were grown by a vertical Bridgman technique using in-house zone refined precursors. The grown crystals were sequentially processed using optimized chemo-mechanical processes to fabricate planar and Frisch collar detectors. Infrared transmission and scanning electron microscopy studies have shown that EIC grown CZT and CdTe crystals have significantly lower Te inclusions and defect densities than commercially available spectrometer grade crystals. The charge transport properties (electron and hole mobility-lifetime products, mutaue & mutauh) of various detectors have been evaluated by Hecht analysis. The detectors have been tested for spectral response using 59.5 and 662 keV gamma-ray sources. The CZT detectors with planar electrodes showed 2.6% FWHM at 662 keV. By adding a Frisch collar, the detectors' spectra improved significantly. The Frisch collar detectors proved to be very promising for assembling large-area arrays with excellent energy resolution at relatively low manufacturing cost.},
keywords = {CdTe, Characterization, Crystal, CZT, Detector},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
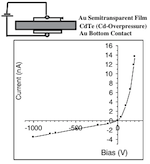
Mandal, Krishna C.; Kang, Sung Hoon; Choi, Michael; Wei, Jiuan; Zheng, Lili; Zhang, Hui; Jellison, Gerald E.; Groza, Michael; Burger, Arnold
Component Overpressure Growth and Characterization of High-Resistivity CdTe Crystals for Radiation Detectors Journal Article
In: Journal of Electronic Materials, vol. 36, pp. 1013-1020, 2007.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: CdTe, Characterization, Crystal, Detector, Growth
@article{Mandal2007b,
title = {Component Overpressure Growth and Characterization of High-Resistivity CdTe Crystals for Radiation Detectors},
author = {Krishna C. Mandal and Sung Hoon Kang and Michael Choi and Jiuan Wei and Lili Zheng and Hui Zhang and Gerald E. Jellison and Michael Groza and Arnold Burger },
url = {http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11664-007-0164-y},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-07-06},
journal = {Journal of Electronic Materials},
volume = {36},
pages = {1013-1020},
abstract = {Spectrometer-grade CdTe single crystals with resistivities higher than 109 Ω cm have been grown by the modified Bridgman method using zone-refined precursor materials (Cd and Te) under a Cd overpressure. The grown CdTe crystals had good charge-transport properties (μτ e = 2 × 10−3 cm2 V−1, μτ h = 8 × 10−5 cm2 V−1) and significantly reduced Te precipitates compared with crystals grown without Cd overpressure. The crystal growth conditions for the Bridgman system were optimized by computer modeling and simulation, using modified MASTRAPP program, and applied to crystal diameters of 14 mm (0.55′′), 38 mm (1.5′′), and 76 mm (3′′). Details of the CdTe crystal growth operation, structural, electrical, and optical characterization measurements, detector fabrication, and testing using 241Am (60 keV) and 137Cs (662 keV) sources are presented.},
keywords = {CdTe, Characterization, Crystal, Detector, Growth},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2006
Mandal, Krishna C.; Kang, Sung Hoon; Choi, Michael; Bello, Job; Zheng, Lili; Zhang, Hui; Groza, Michael; Roy, Utpal N.; Burger, Arnold; Jellison, Gerald E.; Holcomb, David E.; Wright, Gomez W.; Williams, Joseph A.
Simulation, modeling, and crystal growth of Cd0.9Zn0.1Te for nuclear spectrometers Journal Article
In: Journal of Electronic Materials, vol. 35, pp. 1251-1256, 2006.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Crystal, CZT, Growth, Modeling, Simulation, spectrometer
@article{Mandal2006,
title = {Simulation, modeling, and crystal growth of Cd0.9Zn0.1Te for nuclear spectrometers},
author = {Krishna C. Mandal and Sung Hoon Kang and Michael Choi and Job Bello and Lili Zheng and Hui Zhang and Michael Groza and Utpal N. Roy and Arnold Burger and Gerald E. Jellison and David E. Holcomb and Gomez W. Wright and Joseph A. Williams },
url = {http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11664-006-0250-6},
year = {2006},
date = {2006-06-01},
journal = {Journal of Electronic Materials},
volume = {35},
pages = {1251-1256},
abstract = {High-quality, large (10 cm long and 2.5 cm diameter), nuclear spectrometer grade Cd0.9Zn0.1Te (CZT) single crystals have been grown by a controlled vertical Bridgman technique using in-house zone refined precursor materials (Cd, Zn, and Te). A state-of-the-art computer model, multizone adaptive scheme for transport and phase-change processes (MASTRAP), is used to model heat and mass transfer in the Bridgman growth system and to predict the stress distribution in the as-grown CZT crystal and optimize the thermal profile. The model accounts for heat transfer in the multiphase system, convection in the melt, and interface dynamics. The grown semi-insulating (SI) CZT crystals have demonstrated promising results for high-resolution room-temperature radiation detectors due to their high dark resistivity (ρ≈2.8 × 1011 Θ cm), good charge-transport properties [electron and hole mobility-life-time product, μτe≈(2–5)×10−3 and μτh≈(3–5)×10−5 respectively, and low cost of production. Spectroscopic ellipsometry and optical transmission measurements were carried out on the grown CZT crystals using two-modulator generalized ellipsometry (2-MGE). The refractive index n and extinction coefficient k were determined by mathematically eliminating the ∼3-nm surface roughness layer. Nuclear detection measurements on the single-element CZT detectors with 241Am and 137Cs clearly detected 59.6 and 662 keV energies with energy resolution (FWHM) of 2.4 keV (4.0%) and 9.2 keV (1.4%), respectively.},
keywords = {Crystal, CZT, Growth, Modeling, Simulation, spectrometer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}